Mission full.
NASA efficiently crashed a spacecraft into an asteroid Monday, marking a win for the company’s plan for when a devastating asteroid ought to ever threaten humanity.
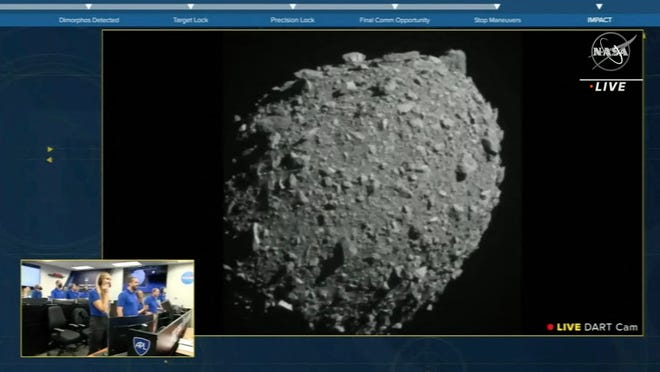
The 1,260-pound Double Asteroid Redirection Check spacecraft, or DART, collided with the estimated 11 billion pound, 520-foot lengthy asteroid Dimorphos at 14,000 miles per hour near 7 million miles from Earth. The spacecraft hit about 55 ft from the asteroid’s heart.
The spacecraft had launched its digital camera and a shoebox-size companion, LICIACube, over every week in the past to {photograph} the mission, which confirmed the influence.
“This was a very laborious know-how demonstration to hit a small asteroid we have by no means seen earlier than, and do it in such spectacular style,” Nancy Chabot, planetary scientist and mission crew chief at Johns Hopkins College, mentioned after the influence.
The finished mission culminates a 10-month-long journey for DART, which value $325 million. The asteroid orbits a bigger one named Didymos, and the 2 have been chosen as a result of they do not pose any menace to Earth.
“There was a variety of innovation and creativity that went into this mission, and I consider it will train us how someday to guard our personal planet from an incoming asteroid,” mentioned NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson. “We’re exhibiting that planetary protection is a worldwide endeavor, and it is rather potential to save lots of our planet.”
VISUAL EXPLAINER: Go inside NASA’s plan to crash the DART spacecraft into an asteroid
The DART crew mentioned no changes have been wanted on the mission and it went down “straight down the center of what our expectations have been.”
Whereas DART efficiently hit Dimorphos, NASA will not know for weeks – probably months – in regards to the collision results.
“Some issues will doubtless come out in even days, possibly weeks,” mission programs engineer Elena Adams instructed reporters following the influence. “However I might say for the quantitative full reply, a few months.”
The company’s objective was to not destroy the asteroid, however fairly shift its orbit round about Didymos sufficient that it modifications each of their trajectories. Dimorphos completes an orbit round Didymos in 11 hours and 55 minutes; NASA hopes the collision shortens its orbit by 10 minutes.
However altering an asteroid’s orbit by simply 1% may very well be sufficient if a damaging one have been headed in direction of Earth, NASA says. At present, there are practically 30,000 near-Earth objects in our photo voltaic system, in response to NASA, which means they arrive inside 120.8 million miles of our planet. Over 10,000 of near-Earth objects them round the identical measurement as Dimorphos.
Planetary protection specialists want nudging a threatening asteroid or comet out of the way in which, given sufficient lead time, fairly than blowing it up and creating a number of items that would rain down on Earth. A number of impactors may be wanted for large area rocks or a mixture of impactors and so-called gravity tractors, not-yet-invented units that may use their very own gravity to tug an asteroid right into a safer orbit.
Whereas no asteroids of that measurement are anticipated to hit Earth within the subsequent 100 years, solely 40% of these asteroids have been found as of October 2021, NASA says. Fewer than 1% of the hundreds of thousands of smaller asteroids, able to widespread accidents, are recognized.
However for now, astronomers say humanity ought to really feel protected.
“Our first planetary protection take a look at was a hit,” Adams mentioned. “Earthlings ought to sleep higher.”
Contributing: Related Press
Comply with Jordan Mendoza on Twitter: @jordan_mendoza5.





